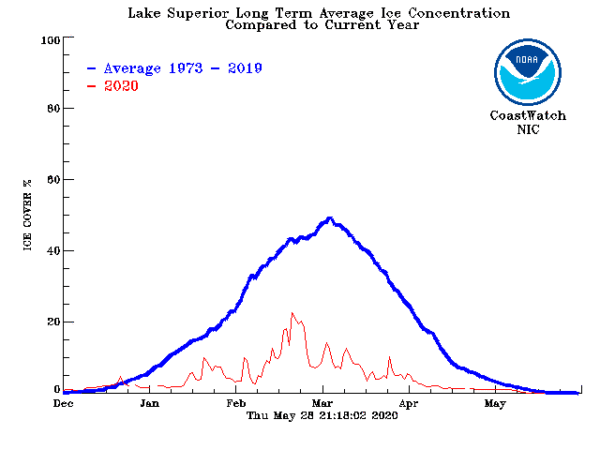
In order to understand ice formation and the types of ice in the Great Lakes, researchers and stakeholders use Synthetic Aperture Radar (SAR) data from the NOAA CoastWatch Great Lakes Node to monitor the ice conditions such as six different types of ice, ice thickness, and ice cover.
Available ice products:
ICECON (Ice Type)
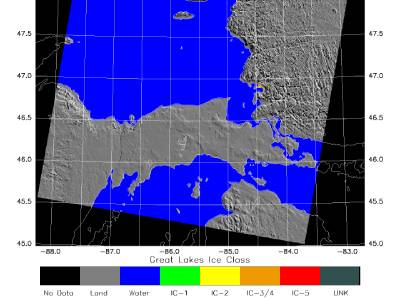
Ice Statistics